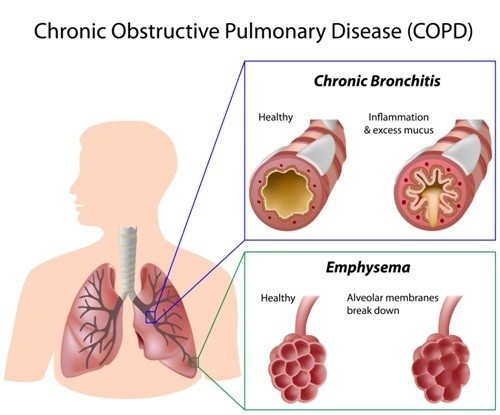
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease constitutes three various conditions like emphysema, chronic asthma and chronic bronchitis. In each of these conditions there is a chronic obstruction of flow of air through the lungs and airways of the human respiratory system which may progress over time.
COPD Definition
COPD is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease which causes chronic obstruction through the airways and lungs of the human beings. This disease features three different obstructions like chronic asthma, emphysema and bronchitis. If asthma left untreated, the airway obstruction become fixed for the patients and chronic inflation is caused. The asthma patients would then have abnormal airflow which leads to airway obstruction called COPD.
Types of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic bronchitis: Chronic bronchitis involves swelling of the inner lining or tube of the airways which leads to the obstruction of airways; this chronic bronchitis also involves inflation. The inflation stimulates production of sputum which triggers the airway obstruction and the obstruction with the mucus increases the chances of bacterial lung infections. Clinically, this is defined as a daily cough which may lasts for up to two years continuously.
Chronic asthma: Chronic asthma is again a disease of airways of the respiratory system which causes obstruction due to the inflation of the airways and the spasm of muscles around the airways. This condition is called bronchospasm in asthma and the inflation of the airways may lead to the thickening of the inner walls which then involves inflammatory cells and mediators to involve in chronic bronchitis. Medications like inhaled steroids are needed to cure this type of chronic obstruction.
Emphysema: Emphysema is a permanent enlargement of the alveoli of the respiratory system which causes the destruction of the walls. This destruction leads to reduce the elasticity of the lung all over. This results in collapse of bronchitis and obstruction out of airflow of the alveoli of the lungs. Air become trapped and minimizes the ability of the lung to shrink and expand during inhalation and exhalation. Hence, patients would feel difficulty in breathing or in exchange of carbon-dioxide and oxygen in and out of the lungs.
Symptoms of Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Patients would develop cyanosis (blue color sign in nail buds and lips) due to a lack of oxygen in blood
- Weight loss due to the excess energy loss in breathing
- Morning headaches due to the retain of carbon-dioxide in the body
- Some patients may couch up blood (hemoptysis)
- Pulmonary hyper tension which is the elevated pressure in the blood vessels, pneumonia or respiratory malfunctions
- Chronic cough and spuntum production is common among chronis bronchitis patients
- Shortness of breath would be found among patients of emphysema
- Frequent respiratory infections
Stages of COPD diagnosis
The stages of COPD diagnosis include chest x-ray, CT scan, computerized tomography, tests for lung functions, pulmonary functions tests to identify the lung disease and calculation of amount of carbon-dioxide and oxygen levels in the blood.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treatments
Bronchodilators:
Bronchodilators are medications that help relax the muscles surrounding the airways and help in opening the airways. Bronchodilators can be taken orally, administered intravenously or inhaled. Inhaled Bronchodilators are more effective because they directly reach the airways and has very less side effects compared to the oral Bronchodilators.
Verenicline:
Verenicline or chantix is a COPD medication for aid in smoking cessation. These medications works by minimizing the pleasure of smoking and reducing the symptoms of withdrawal that triggers the smokers to light up again.
Beta Agonists:
This is the one of the fist medications used for asthma and is still used in certain emergency situations, but may have some side effects like nausea, vomiting and headaches etc. Hence it is not recommended to use in treatment of COPD, but are occasionally given in emergency situations.
Anti cholinergic agents
Acetylcholine is one of the chemicals released by the nerves which affect the muscles around the airway to contract and to expand during inhalation and exhalation processes. Drugs like Ipratropium bromide would help to dilate airways and relax the muscles around it and prevent them from narrowing.
Methylxanthines
Some of the examples of Methylxanthines are aminophylline, theo-dur, slo-bid, uniphyl, theo-24 etc. These medications soothe the airway muscles and prevent them from shrinking and also prevent the mast cells around the airways from releasing chemicals like histamine. This process would increase the force of contraction and expansion of the muscles around the airways and help to cure the obstructions.
Causes of COPD
Smoking is the major cause for COPD and is found to be 15% of cigarette smokers would develop COPD and the death rates of COPD smokers are higher than the non smoking COPD patients. More frequent respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, continuous cough, seines etc are common among smoking COPD patients.
Air pollution
Pollutants like silica and cadmium raise the rates of COPD and the occupational pollutants like construction work pollutants, cotton industry pollutants, coal mining pollutants, metal and steel mining pollutants would trigger the risk of COPD.
Alpha 1 Antitrypsin
AAT is a range of inherited genetic disorder which would leads to COPD. The elastic fibers of the lungs are responsible for breathing and proper flow of air through the airways and in alveolar walls. AAT produced by the liver would cause damage to the elastase on elastin and would block the air flow through the airways. This would lead to obstruction or COPD.
Guidelines for prevention of COPD
Sufficient oxygen is the basic requirement of proper functioning of tissues and hence it is advisable to undergo oxygen therapy to prevent COPD. This is a protective mechanism in the lung that causes constriction of blood vessels in the areas of lung that have low concentration of oxygen. This therapy can prevent COPD exaceration to a great extent.
Conclusion
Oxygen requirements may vary from patients to patients with COPD. It is advisable to consult your doctor before the condition get worse. COPD disease is fully treatable with normal medication alone.